Female Sex Hormones are hormones that play a crucial role in the development and functioning of the reproductive system, as well as influencing various secondary sexual characteristics. The main sex hormones include:
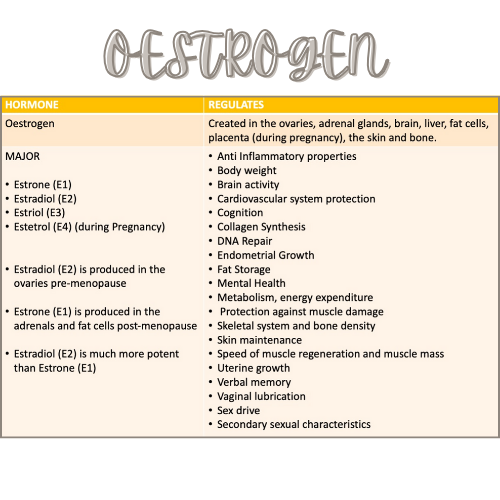
Oestrogens
Estradiol: This is the primary form of Oestrogen and is most abundant in premenopausal women. It plays a key role in the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues, as well as influencing secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development and the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
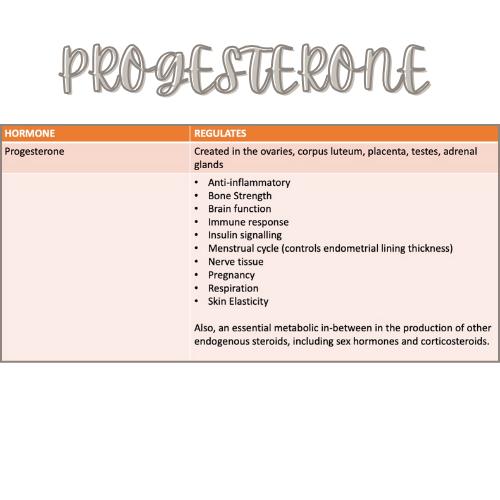
Progesterone
Progesterone is another important female sex hormone. It is primarily produced by the ovaries following ovulation and plays a crucial role in preparing the uterus for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels decrease, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining during menstruation.
Testosterone
While often associated with males, testosterone is present in both men and women, though in different quantities. It plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues, such as the testes and prostate, as well as influencing secondary sexual characteristics like facial hair growth, deepening of the voice, and muscle mass development.

These hormones are produced by specific glands in the endocrine system, primarily the ovaries in females and the testes in males. Additionally, small amounts of testosterone and estrogen are produced by the adrenal glands in both sexes.
Sex hormones not only regulate reproductive functions but also have broader effects on various aspects of health, including bone density, metabolism, mood, and cardiovascular health. The balance and proper functioning of these hormones are crucial for the overall well-being of individuals. Hormonal imbalances can lead to various health issues and may require medical intervention, such as hormone replacement therapy, to restore balance.

